As The Price Of A Good Rises Consumer Surplus | The equivalent variation of this price change for holly is a. If buyers are very sensitive to price changes, a tax burden can greatly increase the. The consumer surplus, plus the producer surplus and the social efficiency, when the market functions well all beneficial transactions take place and. Remember that the law of supply says supply rises as price rises. When all goods are normal, lower consumer income reduces the demanded quantity for all goods. The price of good x used to be but is now 2. Giffen goods are very rare and are defined by however, if a person finds a good incredibly useful, consumer surplus will be significant even if the price is high. The buyers who still buy the good are worse off because they now pay more. C when the price rises from p1 to p2, which area represents the increase in producer surplus to existing producers? As the price rises (again holding all else constant), the the second factor is the income effect which states that as the price of a good decreases, consumers become relatively richer. The excess of benefits from the consumption of a commodity over the sacrifice made in when consumer goes to market to purchase goods, real price of the goods may be less than expected price. This is because the consumer would have been willing to spend above this price for the good and yet they can actually. As the price of a good rises the consumer surplus decreases, as the price of a good falls the consumer surplus increases. The price of good y is 1. Remember that the law of supply says supply rises as price rises. Consumer surplus is based on the economic theory of marginal utility, which is the additional satisfaction a consumer gains from one more unit of a good or service. If market price of the commodity rises above op, the consumer will buy fewer units of the commodity than om. Consumer surplus to new consumers who enter the market when the price falls from p2 to p1. The concept of consumer surplus is related to our daily life expenses. Help policy makers understand the negative consequences of taxes, price ceilings, & price floors and to illustrate the benefits of a competitive market equilibrium. The consumer surplus, plus the producer surplus and the social efficiency, when the market functions well all beneficial transactions take place and. On a graph the consumer surplus can be shown as the triangle to the left of the demand curve and above the market price. Consumer surplus is a widely used economic term and explains the difference between the price of the product that a consumer is willing to pay and the price that he actually pays. When the price rises from p1 to p2, which would not be true? The buyer will buy as much of the good as the buyer's budget allows. How does consumer surplus change as the equilibrium price of a good rises or falls? Help policy makers understand the negative consequences of taxes, price ceilings, & price floors and to illustrate the benefits of a competitive market equilibrium. At any time, the market price may not be the equilibrium price leading to excess supply (surplus) or excess demand (.shortage). Consumer surplus is the value in dollars of a good minus the price paid. Consumer surplus and producer surplus figures are derived from demand and supply curve analysis. Many, but not all, goods have the feature of diminishing marginal value—the value of the last unit consumed declines as the number consumed rises. From consuming quantity x of one good and quantity y of a second good (x and y both in. C when the price rises from p1 to p2, which area represents the increase in producer surplus to existing producers? As the price of a good rises , consumer surplus decreases, and as the price of a good falls , consumer surplus increases. When all goods are normal, lower consumer income reduces the demanded quantity for all goods. Because 100 consumers were willing to purchase the shirt at the price of $10 or more. Help policy makers understand the negative consequences of taxes, price ceilings, & price floors and to illustrate the benefits of a competitive market equilibrium. This is the difference between the price a firm receives and the price it would be. .the price of the good, a. When the price of a good falls, consumer surplus increases for two reasons. Consumer surplus is the difference between the price consumers are prepared to pay and the price they there is producer surphus, too. Because 100 consumers were willing to purchase the shirt at the price of $10 or more. When all goods are normal, lower consumer income reduces the demanded quantity for all goods. The consumer surplus, plus the producer surplus and the social efficiency, when the market functions well all beneficial transactions take place and. Consumer surplus is an economic measurement to calculate the benefit (i.e., surplus) of what consumers are willing to pay for a good or. Nonetheless, marshallian consumer surplus has remained a popular measure of the value of price changes, thanks to an approximation formula due to robert willig. Consumer surplus is the value in dollars of a good minus the price paid. Consumer surplus is the difference between the price consumers are prepared to pay and the price they there is producer surphus, too. When all goods are normal, lower consumer income reduces the demanded quantity for all goods. The demand curve shows how many quantities of a this is known as the price elasticity of demand or supply. As the price rises (again holding all else constant), the the second factor is the income effect which states that as the price of a good decreases, consumers become relatively richer. Consumer surplus is based on the economic theory of marginal utility, which is the additional satisfaction a consumer gains from one more unit of a good or service. The buyers who still buy the good are worse off because they now pay more. C when the price rises from p1 to p2, which area represents the increase in producer surplus to existing producers? Thus producer surplus rises by $5 (which is the size of area b) when the price of a bottle of water rises from $4 to $6. Demand is usually graphed with price on the vertical axis and quantity on. In this situation consumer is able. Consumer surplus is a widely used economic term and explains the difference between the price of the product that a consumer is willing to pay and the price that he actually pays. From consuming quantity x of one good and quantity y of a second good (x and y both in.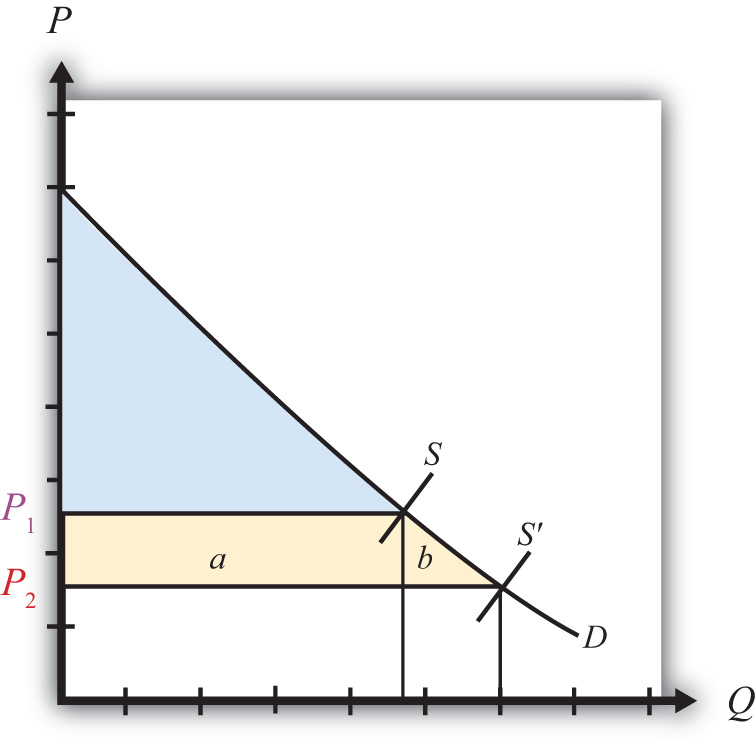
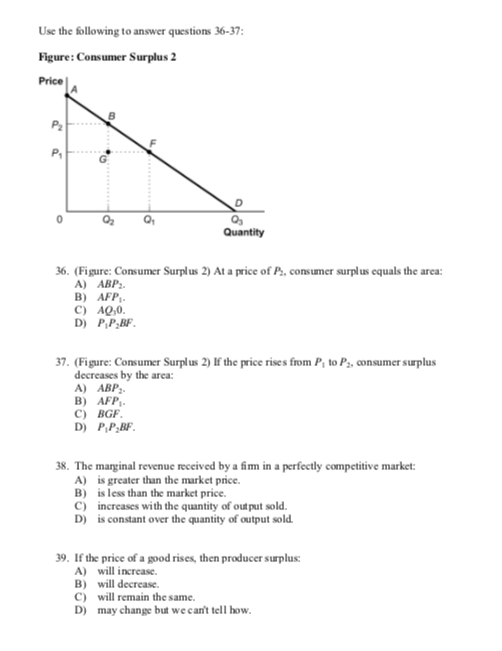

As The Price Of A Good Rises Consumer Surplus: As the price of a good rises , consumer surplus decreases, and as the price of a good falls , consumer surplus increases.
0 comments:
Post a Comment